
Kornylak Corporation
400 Heaton St.
Hamilton, OH 45011
PH: 513.863.1277
TF: 800.837.5676
F: 513.863.7644
Mounting Robot Wheels
Robots
Mounting Wheels
• Robots
• Wheels
<< Back
• Competitions
• Information
• Pictures
• Robot Resources
• FAQ
• Information Request
• Product Literature
• Home
Quick Find:
Robots : Competition | Information | Mounting | Photos | Resources | Wheels
Different Methods for Mounting Robot Wheels
There are numerous ways of mounting wheels on robots. Some are easier to do than others. How you intend to use the wheel determines the method for mounting. For instance, if you are using the wheels as drive wheels, the best method would be a direct connection. How you connect the wheel to the drive shaft can vary on many factors. Some of those factors are: drive shaft size, engine power, weight of robot, etc. Here are a few ways to mount Transwheels and Omniwheels on robots.Idler Mounting
The simplest mounting is the idler mount. This type of mount is for non-powered wheels only. This type of wheel mounting can be thought of like a caster where the wheel is to turn freely. This allows the robot to turn Omni-directionally. Any wheel with a plain bore, bearing, bushing, or axle can be used.
| Mounting Techniques Plain Bore For a plain bore wheel, you would use a shaft that will allow the wheel to turn freely, but without too much play. You may also use spacers to keep the wheel centered. Pros: simple, quick, and easy Cons: if the shaft is too loose or too tight, you will have problems |
 |
| Bushings & Bearings For a wheel with a bushing or bearing you would use a shaft that fits snugly through the bore hole. Secure the wheel to the shaft using lock washers and lock nuts. Here, the goal is for the wheel to turn freely on the bushing or bearing. Pros: simple, quick, easy Cons: if you tighten down on the bushing or bearing too hard, the wheel may not turn |
 |
| Axles The wheels with axles are solid, so the axles must fit into a bracket of some type. This bracket holds the wheel firmly in place, and the wheel turns freely around the axle. Pros: it's a simple concept Cons: if the axle is not held tight it can develop vibrations that may lead to wear and tear |
 |
| Powered Wheels The purpose of the powered wheels is to drive the robot. Powered wheels require more thought when mounting. The mount must be able to handle the torque from the motor, plus the weight of the robot applied to the wheel. Again, there are several options. | |
| Mounting Techniques Keyway Mounting Transwheels with a keyway can be simple if you purchase a mounting kit. A shaft with a key is inserted in the wheel. Two snap rings hold the wheel in place. The shaft is then connected to the motor. This keyway axle kit is available from www.superdroidrobots.com. Pros: It's straight forward and simple. Cons: You have to purchase it from a third party, or make the shaft and key. Over time, the keyway on the wheel may develop some play. |
 |
| Plastic Mount Another method for attaching Transwheels is to screw a plastic spindle to the wheel itself. You have to be careful when using screws. Make sure that they do not pevent the rollers from turning. Pros: straight forward, strong connection Cons: you can damage the wheel if you're not careful |
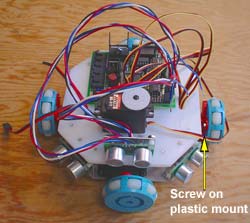 |
| Bolt mounting You can use two bolts to mount the wheel to a spindle that is attached to the motor. It requires you to drill two holes through the wheel. You will need to measure carefully before drilling, and use a drill press. Make sure that the wheel is clamped and secure before drilling. It is also recommended that a large washer be used to help distribute the force. Pros: strong connection with no play Cons: if you are not careful, you can damage the wheel |
 |
| Power Bushing Mount When mounting a bushed wheel as a powered wheel, you can force an oversized shaft through the bushing and then secure it in place with some type of bracket with a set screw or a lock washer and lock nut. This bushing kit is available from www.superdroidrobots.com. Pros: it's fairly simple Cons: you either have to make your shaft or purchase one. If the wheel is stressed too much, the bearing may begin to slip on the shaft |
 |
| Hex Bore Wheels Both the large Omniwheels and the four inch Transwheels offer a hex bore model. A hex bore shaft can be used to drive the wheels. The wheels are held in place by a coupler ring with a set screw. Pros: very simple Cons: attaching the hex shaft to a drive spindle might be a problem |
 |
| Plain Bore Omniwheels Both the plastic and aluminum Omniwheels lock together in pairs. Using a shaft close to the bore size, lock the wheels together using coupler rings with set screws. If you are using a threaded shaft, use a lock washer and lock nuts. Pros: simple, and easy Cons: the couplers or lock nuts and washers need to hold the wheels tight, or else you won't get any traction from the wheel |
 |
![]() Order Kornylak Wheels Online
Order Kornylak Wheels Online
Suggestions to improve our website: Survey
Conveyors | Wheels | Insulation | Vehicles | Products | Literature | Sitemap
Robots | Services | Corporate Facts | Contact Us | FAQ | Info. Request | News
Resources | Links | Directories Links | Organizations Links | Publications Links
Copyright